As healthcare costs continue to rise and insurance coverage becomes increasingly complex, the process of medical billing and payments can be a source of frustration and confusion for both patients and healthcare providers.
In this article, we'll take a closer look at some of the latest statistics surrounding medical billing and payments in the healthcare industry, and explore some of the challenges and potential solutions to these issues. From the high cost of medical debt to the prevalence of billing errors, it's clear that the medical billing and payments system is in need of reform. But where do we begin? Let's delve into the data to get a better understanding of the problem at hand.
The High Cost of Medical Billing and Coding Errors

Medical billing and coding errors can be costly for both patients and healthcare providers. Medical billing errors, many of which are caused by human data entry mistakes, affect a significant proportion of bills and cost the healthcare industry billions of dollars each year.
- According to the most recent available data, it is estimated that 80% of medical bills in the US contain errors (Becker's Hospital Review)
- Poor billing practices result in doctors in the US losing approximately $125 billion per year, or an average of about $5 million per provider (Equifax)
Claims and Billing Errors Can Lead to Insurance Claim Denials

Doctors submit claims to insurance companies to get paid by those companies. They rely on the claims to get accepted so they can collect revenue. However, submitting claims doesn't always guarantee that a doctor will receive payment. Unfortunately, many claims get denied due to errors with coding or billing. Health insurance claim denials are a significant roadblock for healthcare organizations.
- 30% of insurance claims get denied on the first submission (HBMA)
- 32% of denials cited coding as the reason for the denial (Healthcare Finance News)
- It costs $25 on average to re-submit an insurance claim (MGMA)
Manual Data Entry Leads to More Mistakes

Human error is one of the most common reasons for billing mistakes and denied claims. Often private practices have smaller teams running their office, who must juggle multiple responsibilities. They may lack specialized knowledge in medical billing and coding best practices and are usually not up to date on the latest laws, regulations, and industry changes.
- 86% of denials are potentially avoidable (HFMA)
- 34% are considered “absolutely avoidable” (Ibid)
ICD-10 to ICD-11
Since October 2015, ICD-10 has been the standard “handbook” for medical coding and billing of the “Internal Classification of Diseases.” In January 2022, The World Health Organization and its member states implemented a new standard, ICD-11.
ICD-11 has 4x more codes within it than ICD-10 did, and a problem with careless mistakes made by billers and coders already exists. If practices aren't coding correctly, they could be missing out on hundreds of thousands by not coding to the most up-to-date standards. If practices or billers are not trained on coding properly, they could be leaving money on the table!
Medical Billing Errors & The Impact on Patients

Did you know 14 million Americas have medical bills listed on their credit report due to medical billing errors?
- Bills totaling $10,000 or more contained an average error costing $1,300 (ABC News)

This is especially troubling given that patient obligation is over 50% of the healthcare dollar. Research shows that as patient financial responsibility rises, the likelihood of collecting patient payments in a timely manner significantly decreases, making it essential for practices to adopt efficient billing & payment processes.
- Despite the No Surprises Act, 1 in 5 Americans reported receiving a surprise bill in 2022 (MedCityNews)
- Only 20% of all medical consumers will know what they fully owe before treatment (Healthcare.com)
Automating Billing and Coding Can Reduce Billing Mistakes

Automating billing can help to reduce the number of errors by eliminating the need for manual data entry and allowing for real-time checks of billing codes. This can help to ensure that medical bills are accurate and up to date, reducing the risk of overpayment or underpayment.
In addition to improving the accuracy of medical bills, automating billing processes can also help to streamline the billing process, making it more efficient and cost-effective for healthcare providers. This can help to reduce the burden on administrative staff and allow providers to focus on delivering high-quality patient care. By implementing automated billing systems, healthcare providers can help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of their billing processes, ultimately leading to better outcomes for both patients and providers.
- Automating workflows could reduce the processing time by 48% (CPMG Case Study)
- Practices that incorporate automated billing are estimated to save providers approximately $166 billion per year (Ibid)
Medical Billing & Collections: Essential Revenue for Practices

According to the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), 23.2% of a health care organization's revenue is accounted for by collections from patients. That's nearly a fourth of your total annual revenue!
- Roughly 23 million Americans have medical debt (Peterson-KFF)
- Nearly 20% of all Americans who receive health care get sent to collections due to outstanding bills (Consumer Finance Protection Bureau)
- On average, medical bills sent to collections range from $750 to $2600 per person (Ibid)
Important Changes to Patient Collections
Effective July 2022, medical collection debt that has been paid in full by the consumer will no longer be included on US consumer credit reports. Additionally, the time frame before unpaid medical collection debt appears on a consumer's credit report is extended from six months to one year. This gives consumers more time to address their debt and medical practices more time to collect on unpaid bills.
Starting in July 2023, past-due accounts below $500 will no longer be reported on consumer credit reports, making it more critical than ever for providers to implement effective practices for collecting on these balances, as the consequence of impacting a patient’s credit score will no longer exist.
With collecting on past-due A/R accounting for a significant portion of practice revenue, it is crucial to have an effective collection process in place. One way to do this is by notifying patients of their financial obligation as soon as possible, ideally before the visit even occurs.
- 30% of patients walk out of the provider’s door without paying their bill (Becker’s Hospital Review)
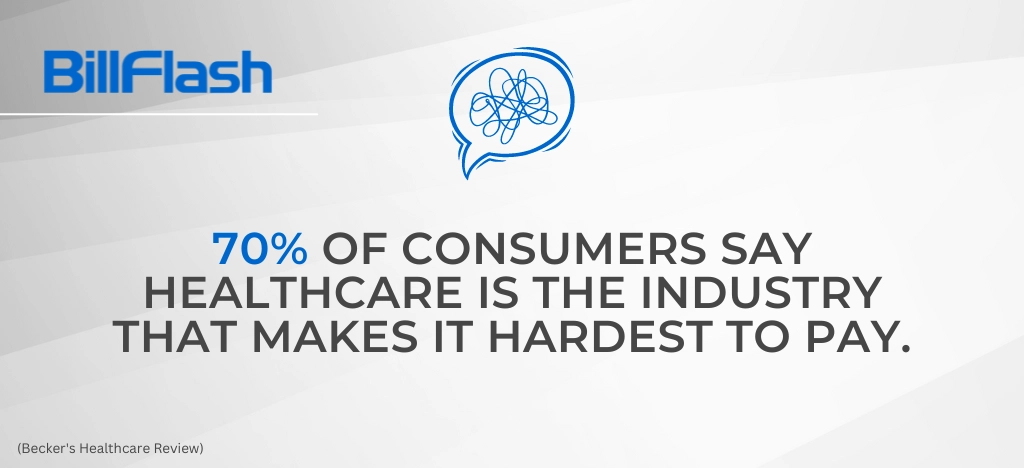
- 70% of consumers say healthcare is the industry that makes it hardest to pay (Ibid)
- 65% of consumers say they would consider switching to a new healthcare provider with a more convenient payment system (Ibid)
Implementing Effective Billing Practices

Sending out statements by mail as soon as possible after treatment helps ensure practices get paid sooner. Implementing electronic statements by email and text also has a significant impact on reducing the average days to payment.
- Sending electronic statements in addition to paper typically cuts the mean days to payment from 20 to 9 and boosts the percentage of full payments rendered 77% to 95%
- 90% of consumers are willing to receive emails and text messages from brands and businesses (Inc.com)
This number should come as no surprise, given the prevalence of mobile devices. Here’s some interesting stats when it comes to SMS marketing:
- People spend roughly four hours each day on their phones
- Within 15 minutes of waking up, 80% of people check their smartphones
- On average, people read 90% of their text messages within the first 3 minutes after receiving them
- 82% of people say they open every text message they receive

Accelerate Payments by Making It Easier for Your Patients to Pay
Offering convenient payment options for patients can help to increase practice cash flow by making it easier for patients to pay their medical bills. By providing a variety of payment options, such as online payment portals or the ability to pay by credit card at the time of service, practices can make it more convenient for patients to pay their bills and reduce the risk of missed or delayed payments. This can help to improve the practice's overall cash flow by increasing the number of timely payments received.
Additionally, offering convenient payment options can also help to improve patient satisfaction, as patients are more likely to pay their bills when it is easy to do so. This can lead to increased patient retention and potentially even new patient referrals for the practice.
- 32% of people will pay their medical bills within five minutes of receiving an electronic notification via text or email (AccessOne)
- Though 74% of consumers prefer to receive medical bills by mail, only 9% prefer to pay them with paper checks (Trends in Healthcare Payments Annual Report)
- 43% of patients are interested in automated payments, yet only 20% of providers reported offering credit card on file capabilities (Ibid)
- 90% of patients plan to pay their bills in full if they are given flexible payment options (Ibid)

Embracing the Future of Healthcare Billing & Payment Processing
By embracing new technologies and implementing automated billing processes, healthcare providers can help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of their billing practices. By offering convenient payment options for patients, practices can also increase their cash flow and improve patient satisfaction. By looking to the future and adopting innovative solutions, the healthcare industry can work towards a more efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centered billing and payment system.
Discover how the BillFlash comprehensive suite of services can automate your end-to-end patient billing, payment, and collections process to maximize your practice’s revenue. Schedule a demo today!

